Osteomalacia
What is Osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia is softening of the bones due to a lack of vitamin D or a problem with the body’s ability to metabolise vitamin D.
What exactly happens in Osteomalacia?
The bones in persons with osteomalacia have a normal amount of collagen, which gives the bones its structure. Since they lack proper amount of calcium, mineralization of bones do not happen leading to softer bones.
What are the causes?
In children, the condition produced by low vitamin D is called “rickets” and in adults “Osteomalacia”
Conditions that may lead to hypovitaminosis D include:
- Not enough vitamin D in the diet
- Not enough exposure to sunlight, which produces vitamin D in the body
- Malabsorption of vitamin D by the intestines
Use of very strong sunscreen, limited exposure of the body to sunlight and smog are factors that reduce formation of vitamin D in the body. The elderly and those who are on antiepileptics are at increased risk for osteomalacia.
Other conditions that may cause osteomalacia include:
- Cancer
- Hereditary or acquired disorders of vitamin D metabolism
- Kidney failure and acidosis
- Liver disease
- Phosphate depletion associated with not enough phosphates in the diet
- Side effects of medications used to treat seizures
Symptoms
- Muscle weakness
- Widespread bone pain, especially in the hip
- Bone fractures that happen with very little injury
Symptoms may also occur due to low calcium levels. These include:
- Numbness around the mouth
- Numbness of arms and legs
- Spasms of hands or feet
- Abnormal heart rhythms
What are the tests to be done?
Blood tests:
Calcium (low), Phosphorus (low), alkaline phosphatase (high), creatinine (normal)with low 25 hydroxy vitamin D3 levels.
Bone x-rays and a bone density test can help detect pseudofractures, bone loss, and bone
softening.
What is the treatment?
Treatment involves oral vitamin D and calcium supplements. Larger doses of vitamin D and calcium may be needed for people who cannot properly absorb nutrients into the intestines.
Regular blood tests may be needed to monitor blood levels of phosphorus and calcium in persons with certain underlying conditions.
What is the prognosis?
Improvement can be seen within a few weeks in some people with vitamin deficiency disorders. Complete healing with treatment takes place in 6 months.
How to prevent?
A diet rich in vitamin D and getting plenty of sunlight can help prevent osteomalacia due to a vitamin D deficiency.
When to Contact an Endocrinologist?
If you have symptoms of osteomalacia or if the vitamin D or calcium levels are very low.
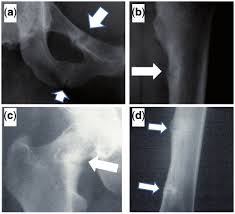
Classical “pseudofractures” (Loosers’ zones) seen in Osteomalacia

