What is “hypoparathyroidism”?
Hypoparathyroidism is an endocrine disorder in which the parathyroid glands do not produce enough parathyroid hormone (PTH), which results in hypocalcemia.
What are the causes?
Postsurgery: Since parathyroid glands are very tiny (difficult to identify) and situated just behind the thyroid gland they are prone for injury/removal during thyroid surgery.
Post hyperparathyroidism surgery
Autoimmune destruction: Usually seen in children/young adults
Very rarely, hypoparathyroidism can be a side effect of radioactive iodine treatment for hyperthyroidism.
Low blood magnesium levels
DiGeorge syndrome: A childhood disease in which hypoparathyroidism occurs because all the parathyroid glands are missing at birth.
What are the symptoms?
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle spasms called tetany (can affect the larynx, causing breathing difficulties)
- Pain in the face, legs, and feet
- Tingling lips, fingers, and toes
- Seizures
- Abdominal pain
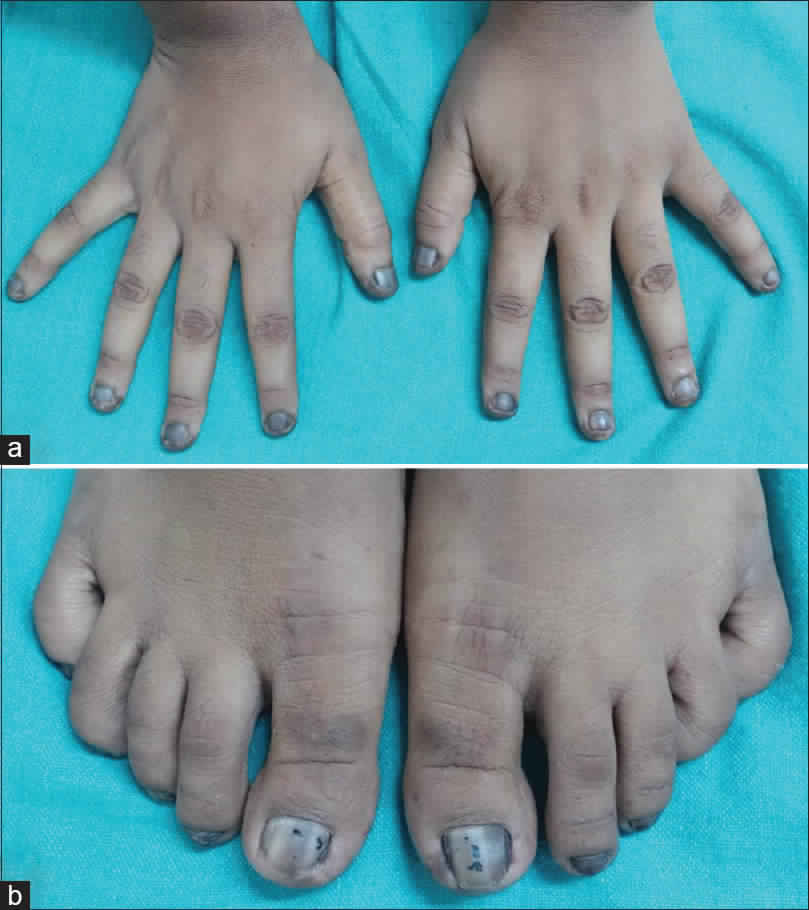
- Brittle nails
- Cataracts
- Dry hair; dry, scaly skin
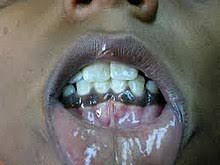
- Weakened tooth enamel (in children)
Additional symptoms may include:
- Decreased consciousness
- Delayed or absent tooth formation
- Hand or foot spasms
What are the tests to be done?
Blood tests:
Calcium (low), phosphorus (high), albumin (usually normal), alkaline phosphatase (normal) and parathyroid hormone (PTH) (usually low).
What is the treatment?
The goal of treatment is to restore the calcium levels in the body.
Treatment involves calcium carbonate and active vitamin D supplements, which usually must be taken for life. Blood levels are measured regularly to make sure that the dose is correct. A high-calcium, low-phosphorous diet is recommended. Regular monitoring (once in 3 months) with serum calcium and phosphorus levels and regular checking (once in 6 months) for excess calcium excretion in urine are very much essential.
Persons who have life-threatening attacks of low calcium levels or prolonged muscle contractions are given calcium through a vein (IV). Precautions are taken to prevent seizures or larynx spasms. The heart is monitored for abnormal rhythms until the person is stable. When the life-threatening attack has been controlled, treatment continues with medicine taken by mouth.
What are the possible complications?
Hypoparathyroidism in children may lead to stunted growth, malformed teeth, and slow mental development.
Overtreatment with vitamin D and calcium can cause hypercalcemia (high blood calcium), nephrocalcinosis and may interfere with kidney function.
What is the prognosis?
The prognosis is usually good if the diagnosis is made early. However, changes in the teeth, the development of cataracts, and brain calcifications are irreversible.
When to Contact an Endocrinologist?
If you develop any symptoms of hypoparathyroidism, seizures or breathing problems with low calcium levels you have to consult an Endocrinologist.