How much Calcium and Vitamin D do we need?
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. People normally get vitamin D through sunlight exposure, which
triggers vitamin D production in the skin. Egg yolks and some types of fish such as salmon and mackerel
provide a little amount of vitamin D. People with dark skin, sunscreen use, poor sunlight exposure and
antiepileptic drug usage are prone for vitamin D deficiency.
What is calcium?
Calcium is a mineral which is important for many body functions. Most of the body’s calcium is stored in
the bones and teeth. Good sources of calcium include dairy products such as milk, cheese, paneer and
curds; canned fish with bones; and green leafy vegetables.
Why do we need calcium and vitamin D?
Calcium and vitamin D are needed for maintaining bone strength. Calcium is necessary for building
strong, healthy bones. Vitamin D allows your body to absorb calcium. In calcium and vitamin D
deficiency, bones may not form properly in childhood and can lose mass, become weak, and break easily in adulthood.
How Adrenal Glands are relevant to our body ?
Why is bone health important?
- Chronic loose stools
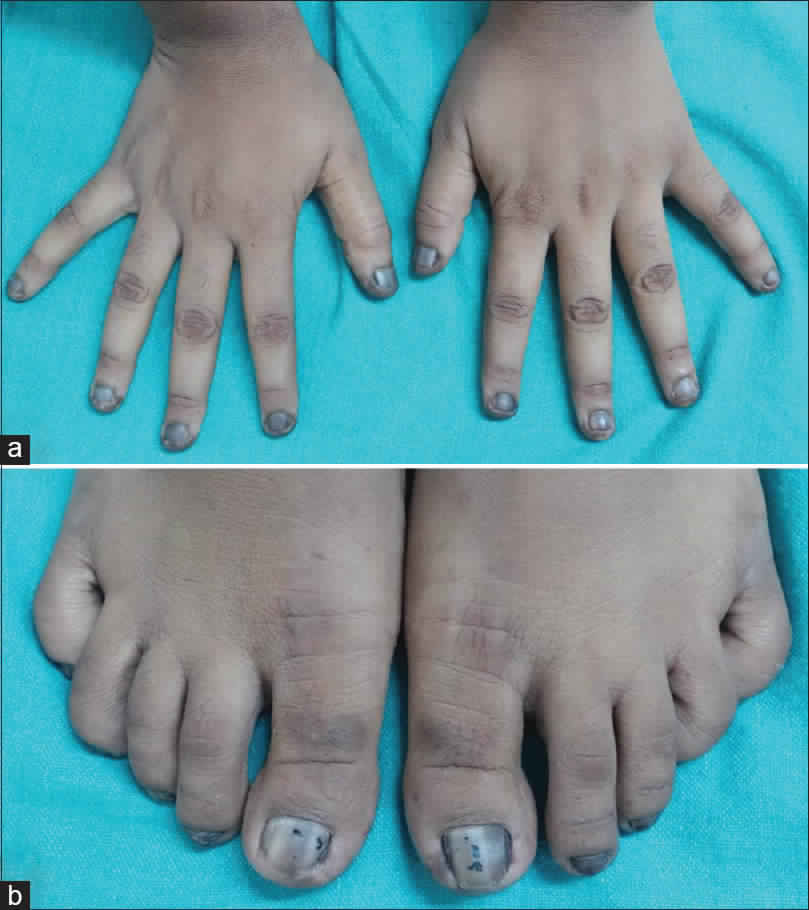
- Darkening of the skin color
- Unnaturally dark color in some places
- Paleness
- Extreme weakness, Fatigue, Loss of appetite
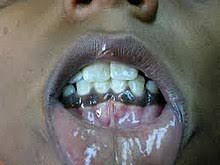
- Mouth lesions on the inside of a cheek (buccal mucosa)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Salt craving
- Unintentional weight loss
- Changes in blood pressure or heart rate
Bone is a tissue that constantly breaks down and gets replaced. Throughout life, the body balances the
loss of bone with the creation of new bone. Highest bone mass is reached at the age of 30 years.
Thereafter, the body begins to lose bone mass. Over time, bone loss can cause “osteopenia” (low bone
mass) and then when it is severe “osteoporosis”, a condition in which bones become weak and are more likely to break (fracture).
How Adrenal Glands are relevant to our body ?
How much is the requirement?
Tests may show :
| Group | Calcium (mg) | Vitamin D (IU) |
| Adults < 50 years | 1000 mg | 400-800 IU |
| Adults > 50 years | 1200 mg | 800-1000 IU |
| Pregnancy | 1500 mg | 1000-2000 IU |
| Lactation | 1500 mg | 1000-2000 IU |
| Children (1-18 years) | 600-800 mg | 600 IU |
- Low sodium and high potassium
- Low BP
- Low cortisol level

Other tests may include:
Calcium and vitamin D rich food must be consumed for better bone health.
Sunlight exposure (at least 10 min/day between 11 AM and 1 PM)is preferred.
In high risk populations (post menopausal women, pregnancy, lactation),
calcium & vitamin D supplementation is a must.
- Abdominal CT scan
- ACTH
How Addison’s disease can be treated?
Steroid replacement will control the symptoms of this disease. However, you will usually need to take these drugs for life. People often receive a combination of glucocorticoids (cortisone or hydrocortisone) and mineralocorticoids (fludrocortisone). More often we come across patients
who stop medications (as they are told by the pharmacy sales persons that steroids have lots of side effects and should not be taken for long time) and land up with various complications.
Steroid medication for this condition should never be skipped because life-threatening reactions may occur.
Sick Day Schedule (Steroid Stress Cover):
Endocrinologist may increase the medication dose in times of stress like:
Infection
Injury
Stress
Usually dosage has to be doubled during any sickness (at least for 2-3 days)
During an extreme form of adrenal insufficiency (adrenal crisis), hydrocortisone must be injected immediately (intravenous/intramuscular).
It is important always to carry a medical identification card that states the type of medication and the proper dose needed in case of an emergency.
How is the prognosis?
When to Contact a Medical Professional ?
Contact your health care provider if:
- Persistent vomiting
- Stressful siyuations such as infection, injury, trauma, or dehydration (dosage adjustment may be needed).
- Undue weight gain
- Ankle swelling (pedal edema).
- Symptoms of adrenal crisis (Abdominal pain, difficulty in breathing, reduced consciousness, low BP)