Cushing syndrome
What is Cushings syndrome?
What are the causes?
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms usually include:
- Visceral obesity (above the waist) and thin arms and legs
- Round, red, full face (moon face)
- Slow growth rate in children
Skin changes that are often seen:
- Purple/violaceous marks (1/2 inch or more wide), called striae, on the skin of the abdomen, thighs, and breasts
- Thin skin with easy bruising
- Acne or skin infections
Muscle and bone changes include:
- Backache
- Bone pain or tenderness
- Collection of fat between the shoulders (buffalo hump/dorsocervical fat pad)
- Thinning of the bones, which leads to rib and spine fractures (osteoporosis)
- Weak muscles
Women often have:
- Excess hair growth on the face, neck, chest, abdomen, and thighs (hirsutism)
- Menstrual cycle becomes irregular or stops
Men may have:
- Decreased fertility
- Decreased or no desire for sex
- Impotence
Other symptoms that may occur include:
- Mental changes, such as depression, anxiety, or changes in behavior
- Fatigue
- Headache
- High blood pressure
- Increased thirst and urination
What are the tests to confirm Cushings syndrome?
Tests to confirm Cushing syndrome:
- Basal serum cortisol (8-9) levels
- Midnight cortisol level
- 24-hour urine free cortisol
Tests to determine cause:
- Plasma ACTH
- Abdominal CT/MRI Pituitary/CT neck, chest and abdomen (Depending upon hormonal levels)
- High-dose dexamethasone suppression test
How do you treat Cushings syndrome?
Exogenous steroid intake related Cushing syndrome: Gradual withdrawal of steroids
Cushings syndrome due to an adrenal tumor is treated with surgery to remove the tumor and often the entire adrenal gland; glucocorticoid replacement treatment is usually needed until the other adrenal gland recovers from surgery. This might be needed for about 9 – 12 months.
If surgery is not possible (such as in cases of adrenal cancer), medicines which can reduce production of cortisol can be given:
- Ketoconazole
- Mifepristone
- Mitotane
- Ankle swelling (pedal edema).
- Aminoglutethimide
How is the prognosis?
Benign adrenal tumors have an excellent outlook after surgery.
In pituitary adenoma, cure rate is about 70% after trans sphenoidal surgery. In case of recurrence, radiotherapy is a good option.
For adrenal cancer, surgery is sometimes not possible. When surgery is performed, it does not always cure the cancer.
When to Contact an Endocrinologist?
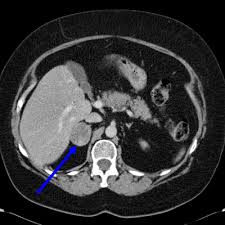
Adrenal adenoma producing Cushing’s syndrome
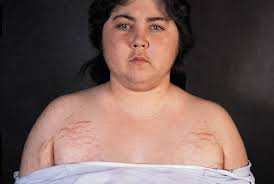
Moon facies, Hirsutism & striae in Cushing’s syndrome

